User Groups (Joomla 2.5)
Joomla! user groups are used to control what users are allowed to do on a site. By assigning permissions to groups, you can allow users to access and edit the back end of your site, create and/or edit articles through the front end or the back end, edit your site’s template settings, and much more. Groups can also be used to control which parts of your site users can see. This article explains how to create new groups and how to assign users to groups.
Creating Groups
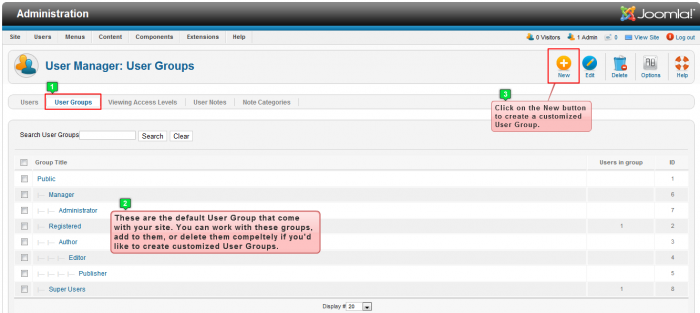
Pre-existing User Groups in Joomla! 2.5
Assigning Users to Groups
Creating Groups
After logging into the back end of your site, go to the User Manager.
Once inside the User Manager, click on the "User Groups" tab. You'll notice a list of pre-existing user groups that come with your site. The next section of this article describes those pre-existing user groups and many site administrators stick with these preexisting user groups, but you can also create custom groups. To do this, click on the "New" button in the toolbar.
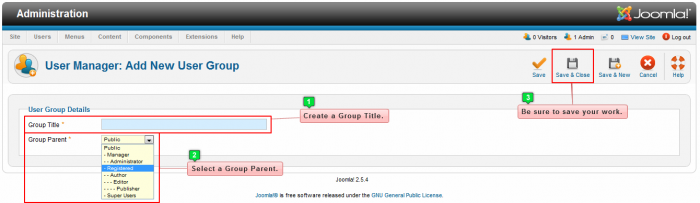
Enter a title for the group and set the "Group Parent" option. The "Group Parent" will determine which permissions this group will inherit. For more information on that subject, please see the article on Permissions Inheritance.
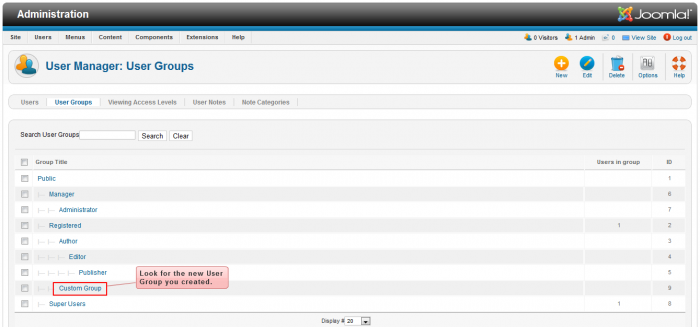
Returning to the "User Manager: User Groups" area you'll see the new user group you created underneath the parent you selected.
Back to Top
Pre-existing User Groups in Joomla 2.5
Joomla 2.5 comes with a number of pre-existing groups that offer out-of-the-box capabilities to assign various levels of access to your Users. Below is an explanation of what each of those pre-existing user groups can do.
Public
Users in the "Public" group can view your site, but cannot perform any administrative actions. Any visitors who view your site, but do not log in, are automatically placed in the "Public" group.
Registered
Registered users can log in to the front end of your site and can view parts of your site that are designated only for registered users. They cannot log in to the back end of your site and cannot perform any administrative actions.
Author
Members of the "Author" group have the same permissions as the "Registered" group. Additionally, they can create new articles, but will not be able to publish them without administrator approval. This means that someone else with higher permissions will have to review and approve those articles before they can be published to your site. They can also edit the articles that they have written, but cannot edit articles written by other authors. Author users cannot log in to the back end of your site.
Editor
Users in the "Editor" group have the exact same permissions as the "Author" group except that they can edit any articles on your site in addition to any articles they have created.
Publisher
"Publishers" have the same permissions as "Editors", except that they can also publish or unpublish any article on your site.
Manager
"Managers" can log in to both the front end and back end of your site. They can create, edit, delete, publish, and unpublish any article or category on your site. They also have access to the Media Manager, as well as the Banners, Contacts, Messaging, Newsfeeds, Search, and Weblinks components.
Administrator
Administrators can log in to both the front end and back end of your site. In the back end, they have access to and can change every aspect of your site except for the Global Configuration. They also cannot modify or delete "Super Users".
Super Users
"Super Users" have complete administrative access to your site. They have access to and can change every aspect of the site. The user that is created by the Joomla site is intially launched is a "Super User".
Back to Top
Assigning Users to Groups
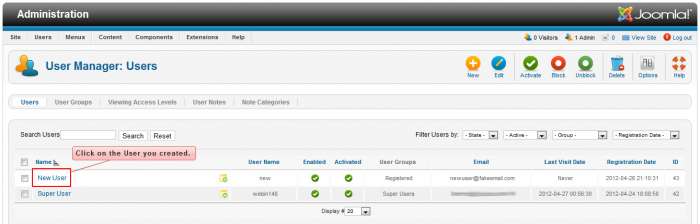
After creating the new user and returning to the User Manager, you can assign that user to a group by opening the user's profile by clicking on the user's name.
In the "Assigned User Groups" area, assign the user to a group by clicking on the box next to the group's name. It is possible to assign a user to multiple groups. Be sure to save your work when you're done.
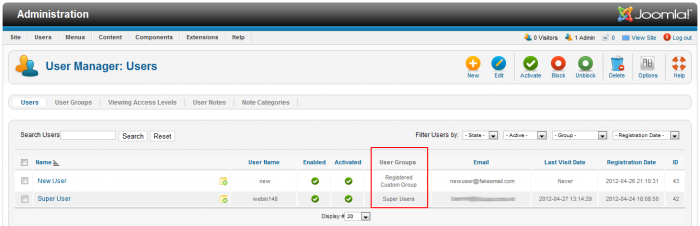
Returning to the "User Manager: Users" area, you'll be able to see each group you've assigned to the new user.
Back to Top

Do you have suggestions for improving this article?
We take a great deal of pride in our knowledgebase and making sure that our content is complete, accurate and useable. If you have a suggestion for improving anything in this content, please let us know by filling out this form. Be sure to include the link to the article that you'd like to see improved. Thank you!